One of the first tasks confronting a new prime minister, after an audience with the king, is to write a “letter of last resort.” Sir Keir Starmer will be asked to write to an (unnamed) commander of a Trident missile submarine on patrol in the Atlantic.
The letter might tell the commander, now uncontactable after a devastating strike on Britain, that the prime minister wished to retaliate by firing a nuclear weapon at the assumed attacker.
Starmer will be asked to write the letter after being “indoctrinated” by the chief of defence staff, Admiral Sir Tony Radakin, who will explain precisely what damage a Trident missile could cause.
Each Trident submarine carries eight missiles with a maximum of 40 warheads, containing more firepower than all the bombs dropped in World War II, including those in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The missiles onboard a Trident submarine could directly cause more than 10 million civilian casualties, with huge disruption to the climate and global food supplies.
Starmer has to write the letter in his own hand, giving detailed instructions about what Britain’s response should be in the event of a pre-emptive nuclear attack on the country.
The letter would be opened by the submarine commander, who would have to conclude that the prime minister was no longer in a position personally to take command of the situation.
The options in the letter are said to include the orders: “Put yourself under the command of the U.S., if it is still there”; “Go to Australia”; “Retaliate”; or “Use your own judgment”.
The procedure is brilliantly exposed in David Grieg’s play, The Letter of Last Resort. It is a conversation between a new prime minister and a senior government official.
The new PM: “Are you saying that in the end it all rests on what I write in this piece of paper now?”
Official: “Yes.”
PM: “To write ‘retaliate’ is monstrous and irrational. To write ‘don’t retaliate’ renders the whole nuclear project valueless”.
Official: “Yes.”
When former Prime Minister Tony Blair was asked to write the letter after his 1997 election victory, he immediately went white. Lord Guthrie, his defence chief, said the briefing made Blair fall “quite quiet”.
Judging by his rhetoric, Starmer would be less anxious. Questioned on June 3 at a campaign hustings in the marginal town of Bury, Starmer said: “Of course I would be prepared to use” nuclear weapons.
Surrounded by candidates who were armed forces veterans, the Labour leader doubled down: “It’s a vital part of our defence. And of course, that means we have to be prepared to use it.”
This rhetoric reinforces his key message: the Labour Party has “changed.” His predecessor Jeremy Corbyn said he would instruct the Trident commander never to press the nuclear “red button”.
"A Monster"

Trident missile system-armed submarine HMS Victorious at home port at HMNB Clyde, Faslane, Scotland, 2013. Photo: Defence Imagery / Flickr / CC BY-SA 2.0.
Starmer may regret expressing such confidence in Trident. Not long ago, the top civil servant at the Ministry of Defence (MoD), Jon Thompson, told MPs that Trident was the project that most kept him awake at night.
It was “the single biggest future financial risk we face”, he said, adding: “The project is a monster.” He warned that it was an “incredibly complicated area to estimate future costs.”
Trident has been predicted to cost a total of more than £200 billion over a 30-year lifespan. The MoD has not challenged the figure and has never given any of its own estimates in public.
This raises a most serious question: far from enhancing the country’s national security, do nuclear weapons actually undermine it?
Trident’s growing cost threatens to overwhelm the entire British defence budget, diverting spending from cheaper conventional weapons systems, such as drones and air defence batteries.
Britain increased spending on nuclear weapons last year by 17 per cent to £6.5 billion, a greater rise than any other nuclear power except the U.S. Over the past five years, British expenditure rose by a staggering 43 per cent.
Trident now costs £12,000 every minute. The National Audit Office warns the cost to renew Britain’s arsenal will rise by more than £99 billion over the coming decade. Yet even these figures might be a fraction of the true cost.
Dominic Cummings, Boris Johnson’s onetime chief adviser, put it this way in a tweet: “All official budget numbers are 100% FAKE cos of the tens of billions in hidden classified budgets from the total shitshow of our nuclear weapons program over 20+ years. Fake budgets, fake debates, fake politics all the way down”.
More recently, Cummings claimed: “Our nuclear weapons infrastructure is dangerously rotting & is tens of billions secretly in the hole, with huge knock-on effects beyond its destructive effects on MoD which has got *even worse* & *even more lying* during the [Ukraine] war.”
He predicted that the “entire puerile election debate will be based on fake budget numbers that will then be given to Starmer on above-STRAP3 [highly classified] yellow paper, with him given the same nudge to classify, punt and lie. Nobody will report on all this & MPs will continue to ignore it…”
This conspiracy of silence is perhaps perpetuated because those charged with overseeing our nuclear arsenal are able to profit handsomely from it when they leave office. There’s an umbilical cord, or “revolving door,” between top security officials and the arms industry.
Chief among them is BAE Systems, which constructs the Trident submarines in Barrow-in-Furness. Their board includes Sir Mark Sedwill, who joined the company in 2022 shortly after he resigned as Britain’s most senior civil servant. Campaign Against Arms Trade found the company recruited dozens of former Whitehall staff, diplomats and ministers.
The special indulgence and absence of accountability surrounding nuclear weapons is reinforced by the lack of competition between arms companies like BAE, which effectively has a monopoly.
"Towering Achievement"
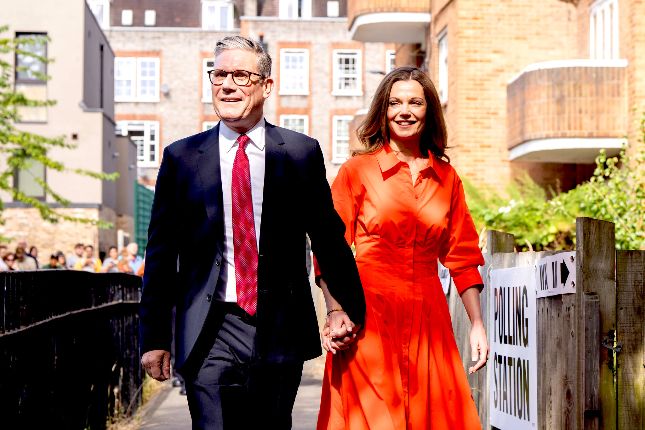

Starmer and his wife Victoria Starmer casting their votes on Thursday in North London. Photo: Keir Starmer / Flickr / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Yet none of these hidden costs or conflicts of interest appears to trouble the new prime minister. In a Daily Mail article, Starmer described the creation of Britain’s nuclear weapons programme as one of the “towering achievements” of Clement Attlee’s post-war Labour government, along with the National Health Service, or NHS, the public health service.
Attlee spent many millions of pounds developing Britain’s first nuclear bomb in a project he kept secret from most of his cabinet colleagues at a time when the country was technically bankrupt.
Then, as now, Britain could not afford both nuclear weapons and the NHS — yet voters were not offered the choice. “Nurses not nukes” could have been a compelling slogan, if the electorate knew what was going on.
The secrecy imposed by both Labour and Conservative governments about the development of nuclear weapons is exposed by a note Winston Churchill received from his scientific advisor Lord Cherwell in 1951.
“Concealment was certainly very necessary at the inception of atomic energy work”, Cherwell wrote. “And frankly I am agreeably surprised that the Socialist Government [ie Attlee’s] was sufficiently imaginative and patriotic to risk the parliamentary criticism to which this might expose them”.
Without an informed cabinet, let alone electorate, to stop it, the first British atomic bomb was tested over the Monte Bello Islands in the Pacific Ocean in 1952. Five years later, Britain tested its first H-bomb on Christmas Island, an Australian territory in the Indian Ocean.
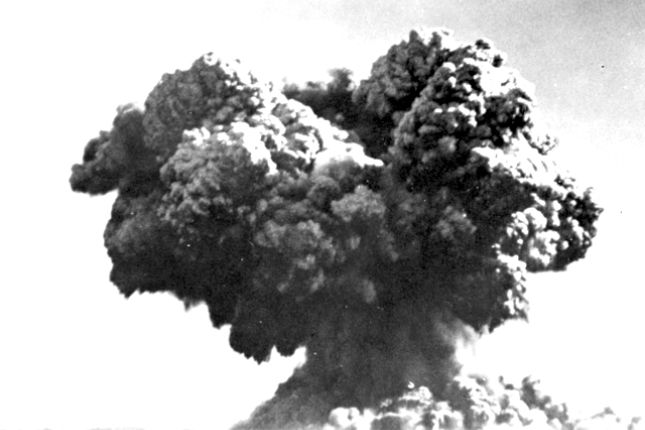

An early stage in the explosion, after the initial orange flash, of Britain’s first atomic weapon test in the Monte Bello Islands, Oct. 3, 1952. Photo: Naval Historical Collection / Wikimedia Commons / Public domain.
Service personnel charged with watching the explosions were not warned of the dangers of radiation, which can cause cancer, heart problems and birth defects. These veterans are still seeking compensation and their medical records.
In 1957, Aneurin Bevan, the architect of the NHS as health secretary but subsequently the shadow foreign secretary, successfully opposed a host of Labour Party motions calling for the end of Britain’s nuclear weapons project.
If passed, he said, Britain “would go naked into the conference chamber” — a reference to international meetings on defence and security. It was a striking, albeit misleading, metaphor, and one that has impressed governments ever since.
The Labour leadership’s support for the bomb was the catalyst for anti-war protests leading to annual Easter marches to the Atomic Weapons Establishment (AWE) at Aldermaston, Berkshire, and the foundation of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND).
It was also closely followed by the foundation of Britain’s “special relationship” with the U.S. — the signing of the Mutual Defence Agreement (MDA) between the two countries in 1958. The MDA, whose full contents remain secret, enshrines Britain’s reliance on the U.S. for essential technology and material without which the Trident system would not function.
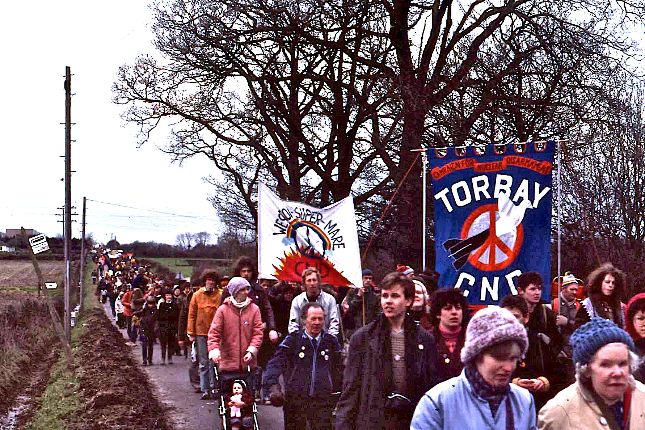

1983 Easter CND march around the Atomic Weapons Research Establishment at Aldermaston in the U.K. Photo: Johnragla / Wikimedia Commons / CC BY-SA 3.0.
The agreement is incorporated in U.S. law, yet despite its fundamental importance to Britain’s relations with its closest ally and its role in the world, it has no legal status in the U.K.
It has never been the subject of a substantial debate or vote in Parliament. It has to be renewed every decade, and will be again this year, probably in a discreet ceremony in Washington, but almost certainly without any meaningful debate in Britain.
Depopulation
The history of Britain’s nuclear arsenal reveals recurring and interlocking themes: the cost, the absolute reliance on the U.S. — giving a lie to claims that the country’s nuclear “deterrent” is independent — and its credibility as a usable military weapon.
Britain’s dependency on the U.S. has been repeatedly enshrined. President John F. Kennedy and Prime Minister Harold Macmillan negotiated a deal in 1962 for the U.S. to supply Polaris nuclear missiles for British submarines.
The pact, drawn up in the Bahamas, was further evidence of Britain’s dependence on the U.S. France’s president, Charles de Gaulle, said it was the main reason he vetoed Britain’s membership of the European Economic Community the following year.
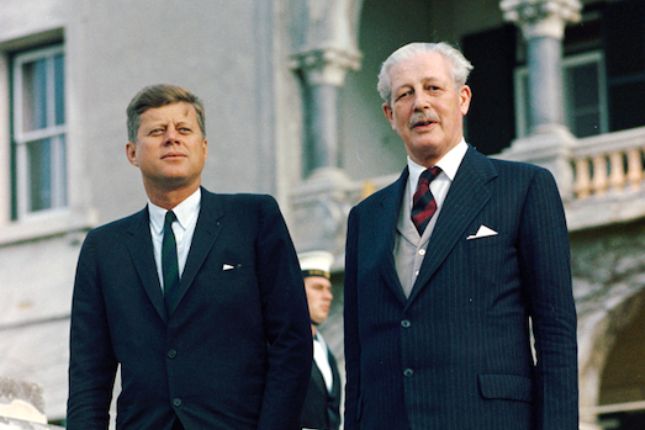

Kennedy and Macmillan in 1961 in Hamilton, Bermuda. Photo: Cecil W. Stoughton / Public Domain / Wikimedia Commons.
The return of a Labour government in 1964 — after 13 years of Conservative rule — posed no threat to the deepening ties between Britain and America over nuclear weapons. Far from it.
Soon after he became prime minister, Labour’s Harold Wilson secretly agreed to a U.S. request to build a bomber base on Diego Garcia, the largest island of the Chagos archipelago in the British Indian Ocean Territory.
Some 1,500 islanders were forcibly displaced, many to Mauritius and Seychelles. In return, the Labour government secretly obtained a discount, believed to amount to around £200 million in today’s money, on the Polaris nuclear missile system.
The dispute over the status of the Chagos islands remains unresolved with Britain rejecting U.N. demands to let the islanders return home.
Wilson also secretly agreed to the Chevaline project, a scheme to make Polaris missiles more likely to penetrate Soviet air defences. Many senior Whitehall defence officials viewed this as an expensive and futile move.
They warned the technology was obsolete from the start, before Labour and Conservative governments wasted hundreds of millions of pounds on it. The Commons public accounts committee reported in 1982 that John Nott, Margaret Thatcher’s defence secretary, said Chevaline’s cost had “gone bananas.”
The project was in the control of unaccountable nuclear scientists, the committee reported. “Our criticism,” it added, “is that the costs were not disclosed, and that there was no requirement that they should be disclosed.”
Nothing has changed.
Thatcher & Blair
Before long, the U.S. developed the Trident nuclear missile system as a successor to Polaris. If Britain wanted to maintain a nuclear arsenal of its own, it had no choice but to follow suit.
In 1980, a year after her election victory, Thatcher agreed to buy Trident missiles for British submarines. She did so without informing her cabinet.
Documents released in 2011 revealed that two-thirds of the cabinet were opposed and even the chiefs of staff were divided.
Nott told Thatcher that a full debate on nuclear defence was essential in light of these divisions. Trade secretary John Biffen privately warned Thatcher not to underestimate the electoral damage the anti-nuclear movement could inflict. A women’s anti-nuclear camp had just been set up at Greenham Common, where U.S. cruise missiles were due to be based and a CND rally attracted 250,000 people.
Thatcher’s cabinet secretary, Sir Robert Armstrong, reassured her that when Macmillan negotiated the deal in the Bahamas with Kennedy to buy Polaris, the cabinet “ratified the decision and the agreement, but played no part in arriving at the original decision or in laying down the negotiating brief.”
He also reminded her that Wilson did not consult his cabinet in 1974 when he agreed to procure the Chevaline system. Thatcher received further support from her first foreign secretary, Lord Carrington, who told the cabinet: “Failure to acquire Trident would have left the French as the only nuclear power in Europe. This would be intolerable.”
That is a view still widely held in Westminster and Whitehall.
Blair had to rely on Conservative MPs in 2007 to pass a vote on replacing Britain’s existing Vanguard-class of nuclear-armed submarines. Eighty-eight Labour MPs disobeyed a three-line whip and voted against the government.
It was the biggest backbench rebellion since the 2003 vote on the invasion of Iraq. At stake was a new fleet of Dreadnought submarines, which would not enter service until the 2030s, and an upgraded version of the Trident missile.
Reflecting on that vote, Blair wrote in his autobiography, A Journey: “The expense is huge and the utility [of Trident is] non-existent in terms of military use.” Although Blair conceded the “common sense and practical argument” against Trident, in the end he thought giving it up would be “too big a downgrading of our status as a nation.”
Breaking International Law?
Retaining nuclear weapons might help Britain justify its place as one of five permanent members in the U.N.’s security council. Yet its reliance on America to maintain a nuclear arsenal should raise questions about its independence and compliance with international law.
Under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), which came into force in 1970, signatories are bound to “prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology.” This commitment is difficult to square with former U.S. President George W. Bush’s comment in 2005 that the U.S. helps Britain maintain a “credible nuclear force.”
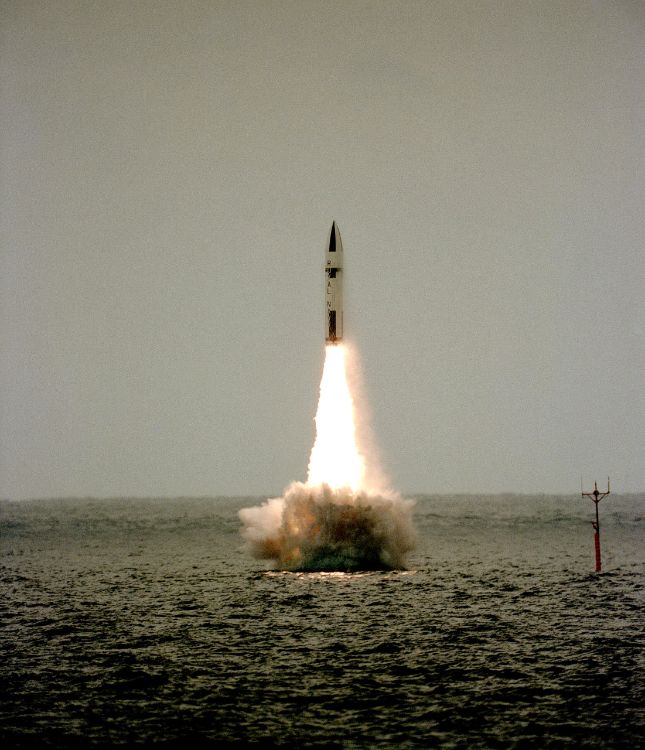

Polaris missile being fired in a flight test from the submerged British nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine HMS Revenge off the coast of Florida near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, June 9 ,1983. Photo: US National Archives / Public Domain / Wikimedia Commons.
American expertise helped install what was said to be the world’s most powerful laser at the atomic weapons establishment in Aldermaston, part of a multi-billion pound scheme designed to enable production of a new generation of nuclear warheads.
The British American Security Information Council, an independent think-tank, believes Whitehall has an “open-ended” arrangement with Washington to “disseminate” information, technology and materials “in pursuit of more sophisticated nuclear weaponry”.
Successive British governments have denied that such cooperation with the U.S. breaches its obligation under the Non-Proliferation Treaty. They claim that the NPT prevents only “wider” spread of nuclear weapons and turn the logic of the treaty on its head. Britain must continue to modernise its nuclear arsenal, officials argue, because nuclear weapons will inevitably spread.
The MoD claimed in a 2003 defence white paper that the “continuing risk from the proliferation of nuclear weapons, and the certainty that a number of other countries will retain substantial nuclear arsenals, mean that our minimum nuclear deterrent capability, currently represented by Trident, is likely to remain a necessary element of our security”.
But two senior lawyers have said there is a strong case that the U.S.-U.K. mutual defence agreement breaches the NPT, as it forbids the transfer of nuclear weapons or devices. Renewal of the MDA, they argued, was intended to “continue and enhance Britain’s nuclear programme”. The lawyers added that the NPT took precedence over U.S.-U.K. agreements under international law.
Blair asked Bush for American help to maintain Britain’s “nuclear delivery system” in 2006. His letter only came to light through a freedom of information request by Peter Burt of Nuclear Information Service nearly a decade later.
Upon seeing the paperwork, Burt said: “The U.K. and U.S. are setting a dreadful example to the rest of the world by renewing the MDA, and are seriously undermining the credibility of international efforts to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons.”
He added: “If Iran and North Korea had signed a similar agreement for the transfer of nuclear weapons technology, the U.K. and U.S. would be branding them pariah nations and screaming for the toughest of international sanctions to be imposed.”
Burt also found a senior American nuclear official had visited Aldermaston and referred to “enhanced collaboration” on “nuclear explosive package design and certification”, on “maintenance of existing stockpiles”, and the “possible development of safer, more secure, warheads”.
Another document describes the MDA as an agreement that enables Britain and the U.S. “nuclear warhead communities to collaborate on all aspects of nuclear deterrence including nuclear warhead design and manufacture”.
Ministers and defence officials argue that “physical movements” under the MDA do not involve nuclear weapons or devices and therefore the agreement does not contravene the letter of the NPT.
While these movements may not involve actual nuclear material, British military aircraft regularly cross the Atlantic with highly radioactive ingredients supplied by the U.S. These ingredients are absolutely vital to the Trident missile system.
Blair-era documents from when he renewed the MDA make it clear Whitehall did not want a debate in Parliament about the military pact. Defence officials worried it would give politicians “an opportunity to raise wider questions concerning…our obligations under the nuclear non-proliferation treaty”.
But the MoD need not have worried. No senior MP, not even members of the Commons defence committee, pressed for a full debate.
Obama to Starmer
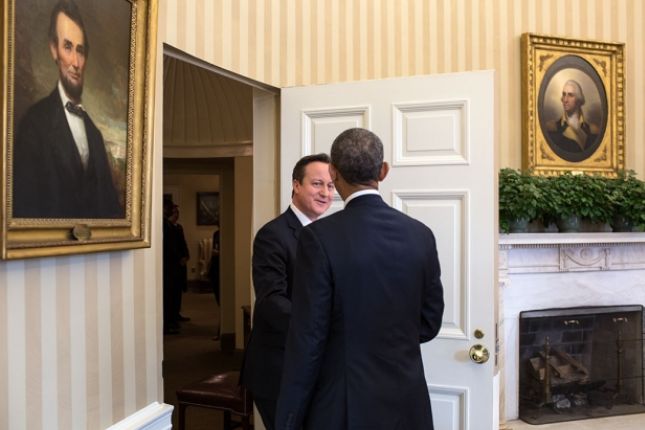

Obama greets U.K. Prime Minister David Cameron in the Oval Office, Jan. 16, 2015. Photo: Official White House Photo by Pete Souza.
The latest 10-year agreement under the MDA was signed in 2014 by British and U.S. officials in Washington. Whitehall was silent. Britons had to rely on a statement by President Barack Obama.
He told Congress the agreement would “permit the transfer between the United States and the United Kingdom of classified information concerning atomic weapons”.
The U.K., Obama added, “intends to continue to maintain viable nuclear forces into the foreseeable future.” It was in America’s interest to continue to help Britain “in maintaining a credible nuclear deterrent”.
There was no word from the Foreign Office, the Whitehall department responsible for updating the U.K.-U.S. treaty. Parliament, a spokesperson said in response to questions, would be informed “at an appropriate time”. That never came.
Revealing the content of the new agreement could “assist proliferation” of nuclear weapons, the Foreign Office claimed.
Some MPs in an all-party Trident Commission took a dim view. They published a report concluding Britain’s deterrent was “a hostage to American goodwill” and the life expectancy of the U.K.’s nuclear capability could be measured in months.
Their report noted that Britain’s Trident missiles were in a common pool shared with the U.S. and maintained in Kings Bay, Georgia, while its nuclear warheads are designed and maintained at Aldermaston but only with the help of U.S. know-how.
They added: “The U.K. is dependent on the United States for many component parts of the guidance and re-entry vehicle, and for [the] ballistic missile system itself”.
Yet in 2016 the Commons voted in favour of Trident by a majority of 355 MPs. Labour’s new leader, Jeremy Corbyn, revolted together with 47 of his MPs, while another 41 were absent or abstained.
Among those to vote no were David Lammy.
He told the Commons then: “Today as a matter of conscience I will be voting against Trident renewal. I simply do not accept that there can ever be circumstances in which it would be permissible to deliberately target millions of innocent civilians in this way.”
Lammy, once a member of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament, added: “I cannot in all conscience vote in favour of writing a blank cheque for billions of pounds today when so many of my constituents are living in deprivation and when public services are stretched beyond breaking point.”
The New Cold War

U.K. Foreign Secretary David Lammy, poses for a photograph on Friday following his appointment to cabinet by Starmer. Photo: Lauren Hurley / No 10 Downing Street / Flickr / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Today he no longer holds this view. Lammy is now “100 per cent behind the U.K.’s nuclear deterrent”, explaining that the access to information he had as a member of the Privy Council — who take an oath of secrecy — had “truly shown him the seriousness of the systemic risk that Vladimir Putin poses to our country”.
“Had Ukraine been allowed to retain their nuclear weapons after its independence from the Soviet Union, they would not have faced the invasion that they did from Putin”, Lammy claimed, referring to a stockpile that had been under Moscow’s control.
He went to Washington after his conversion and met a series of think-tanks. One visit, to talk at the Center for American Progress, cost his benefactors more than £8,000.
Starmer has described his commitment to Britain’s nuclear weapons as “unshakeable” and “absolute”. To drive home the point as he awaited the election starting gun, he told an audience at BAE shipyards in Barrow-in-Furness, where Trident submarines are built: “The U.K.’s nuclear deterrent is the bedrock of Labour’s plan to keep Britain safe”.
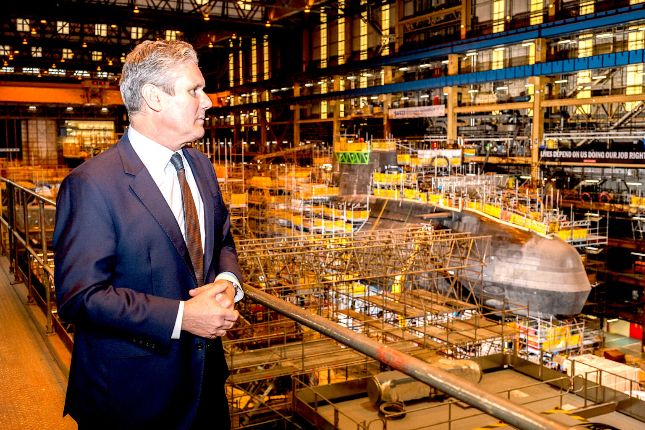

Starmer visiting BAE Systems in Barrow to confirm Labour’s unshakeable commitment to the U.K. nuclear deterrent, April 12, 2024. Photo: Keir Starmer / Flickr / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Such claims are made against the background of growing uncertainty surrounding the cost and reliability, even the purpose, of Trident.
When I asked him about Trident, Lord David Richards, a former head of the army and chief of defence staff, told me: “It is more and more difficult to be persuaded we require it.” Some day other choices would have to be made, he suggested.
Replacing Trident with a new nuclear missile system would no longer be justified if, for example, Britain’s conventional forces were cut so much that the country would become a “Belgium with nukes”.
In 2013, Sir Jeremy Greenstock, former British ambassador to the U.N. in New York, was asked whether possessing nuclear weapons really meant Britain had more influence in world affairs. Influence in the modern world, Greenstock replied, was composed of many things, notably a strong economy. Nuclear weapons was one of the “least relevant.”
Trident has routinely been described by its supporters as the “ultimatum insurance” in the event of an existential threat to Britain. Yet few suggest the government should build many more hospitals as an insurance against a possible — indeed likely — future pandemic.
A Liability?
Shortly before parliament voted to renew Trident in 2016, one of the missiles veered off course during a test that could have had serious consequences. The Royal Navy did not disclose the incident and it only came to light because of a whistleblower. A subsequent £17 million test earlier this year also failed. The missile, fired by HMS Vanguard, landed in the sea close to the launch site.
The test came shortly after Vanguard had spent seven years out of service undergoing a £500 million refit. The maintenance was only meant to last four years, and the overrun saw HMS Victorious tied up awaiting dry dock space.
This left only two of the four boats in the Trident fleet, HMS Vigilant and Vengeance, operational. Britain’s nuclear doctrine relies on a Continuous At Sea Deterrence, meaning one of the submarines must always be deployed.
With fewer boats available, their patrols are lasting for longer — sometimes six months instead of the usual three. Spending so much time underwater, away from their families, places immense stress on the crews’ mental health. It is perhaps not surprising that some have turned to drugs. Nine sailors were removed from HMS Vigilant after testing positive for cocaine.
The project to replace the Vanguard fleet with Dreadnought submarines has also been subjected to delays, putting more pressure on the aging boats. Staff at the naval base housing the U.K.’s nuclear deterrent had to be moved after a serious radiation breach, a whistleblower has alleged.
This state of affairs led Francis Tusa, an experienced defence analyst, to warn in December: “The U.K.’s submarine-based nuclear deterrent is on a knife edge …. so acute that even today, a four boat deterrent — always deemed to be essential to maintain Continuous At Sea Deterrence — has been more of a concept than a reality”.
But if Cummings’ prediction is correct, Starmer will plough on regardless. He is committed to a “triple lock” on Trident: 24/7 patrols, four new submarines and unlimited upgrades. History shows the true cost of all this to the British public will be far more than any “fully-costed” manifesto makes out.
Main photo: Starmer at Number 10 Downing Street on Friday following his appointment © Kirsty O’Connor / No 10 Downing Street / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Source: Consortium News.